China toughens regulation on rejected back-door listing

BEIJING -- The Chinese securities regulator has said it will step up regulation on rejected back-door listing, announcing a cool-down period for firms to restart their public drive.
Businesses that have their first listing rejected will have to wait for no less than three years before trying again, according to a statement on the website of the China Securities Regulatory Commission (CSRC).
The back-door listing refers to the process that a privately-held company gets included into a stock exchange by purchasing a publicly-traded company.
The CSRC said it will also strengthen supervision over other types of failed initial public offerings (IPOs), with the focus on information disclosure about rectifications and changes in financial reports.
To improve the quality of public firms, the securities regulator has started rigorous approval procedures for IPOs since a new review committee came into office in October, rejecting or suspending more than half of IPO applications. The hard-lined stance is considered part of the country's financial clean-up.
China's top legislature plans to prolong a mandate, which allows the State Council to make adjustment for reforms that will change the stock listing system from approval-based to registration-based, for another two years to Feb 29, 2020.
- Domestic single-dose flu drug approved
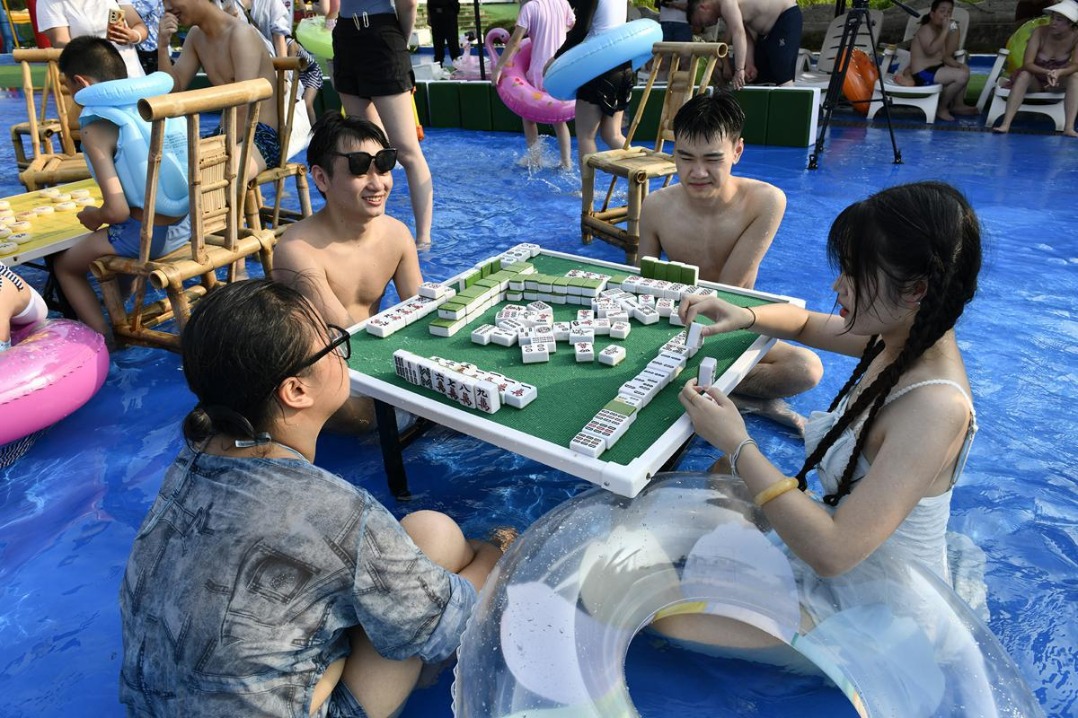
- Water mahjong games cool visitors in Chongqing
- Sanya to host sixth Asian Beach Games in April
- Guangdong, Hong Kong and Macao to jointly hold entrepreneurship competition
- China approves rice-derived recombinant human albumin injection
- Hundreds attend 5th TCM Culture Festival in Tianjin