Soil invertebrates can be climate warriors, finds study

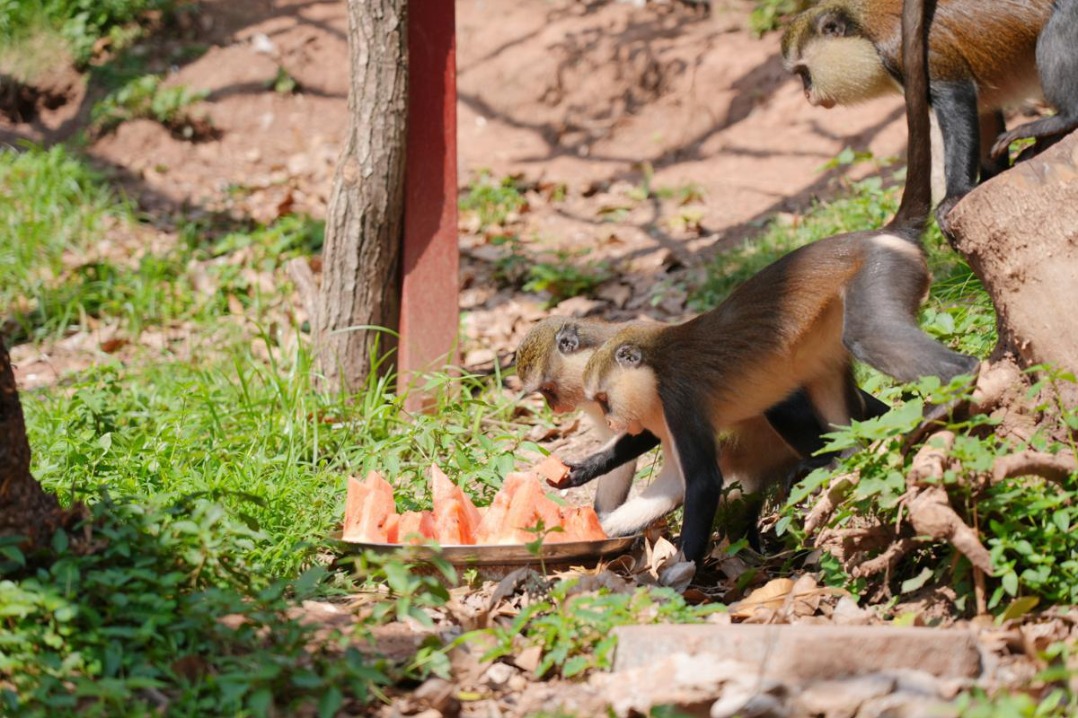
A Chinese-foreign research team has discovered that soil invertebrates — such as termites, ants, and earthworms — play a crucial role in enhancing soil fertility, improving soil structure and increasing crop yields. These organisms are vital for global element cycling, material decomposition and biodiversity conservation.
The findings, which offer new insights into addressing climate change and promoting ecological restoration, were published in the journal Nature on Wednesday. The paper, titled "Global Engineering Effects of Soil Invertebrates on Ecosystem Functions," was led by Wu Donghao, a postdoctoral fellow at Sun Yat-sen University in Guangdong province. Chu Chengjin, a professor from the university's School of Ecology, is the corresponding author.
Co-authors include Du Enzai, a professor at Beijing Normal University; Nico Eisenhauer, a professor from the German Centre for Integrative Biodiversity Research; and Jerome Mathieu from the Sorbonne University of France.
Termites, ants and earthworms, known as "ecosystem engineers", are found in various ecosystems worldwide. They create unique biological structures like ant mounds, mud covers and worm castings through soil disturbance. These activities are essential for nutrient cycling and maintaining biodiversity, the paper says.
The study shows that globally, the activities of these invertebrates significantly increase the content of major nutrients such as soil carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, sodium and magnesium. They also improve multiple soil indicators, including soil conductivity, soil respiration rate, microbial biomass and plant biomass.
Wu explained that the team spent a year collecting and screening 1,047 relevant studies from six continents, extracting 12,975 data records for meta-analysis.
The research found that rising annual average temperatures enhance the impact of termites on soil respiration and plant biomass, while earthworms show increased effects on soil nitrogen and phosphorus content.
In contrast, the positive effects of ants on soil nitrogen and phosphorus content, plant biomass, and plant survival rates decrease with increasing plant biomass, peaking in mid-latitude regions.
Further analysis revealed that termites boost plant growth by alleviating phosphorus limitations in tropical areas, while ants enhance plant growth by mitigating nitrogen limitations in temperate regions.
"This means future climate warming may enhance soil respiration and plant productivity by stimulating termite activity. The effects of termite soil engineering on carbon cycling and carbon source-sink dynamics should be taken seriously," Wu said.
He added that protecting and adding specific soil invertebrate groups in different climate zones can help enrich specific nutrients and promote crop growth.
However, under the influence of human activities and climate change, the number of soil invertebrates is dwindling or facing extinction, yet surveys and conservation efforts remain insufficient, he said.
"Our research highlights the importance of protecting soil invertebrates, showing it will help improve agricultural production, address climate change, promote ecological restoration and achieve sustainable development," Wu concluded.
Chu noted that further research on these "soil engineers" will explore differences among various invertebrates in promoting plant growth through experiments.
- China takes strong measures to ensure affordable medicines during 14th Five-Year Plan period
- China issues typhoon and rainstorm warning
- Woman extends a thousand hands to Wuxi expats
- China boosts medical insurance spending on innovative drugs
- Long-term care insurance covers 190 million people in China
- How to wear Shanghai-style qipao in daily life?