China launches its first asteroid sampling mission
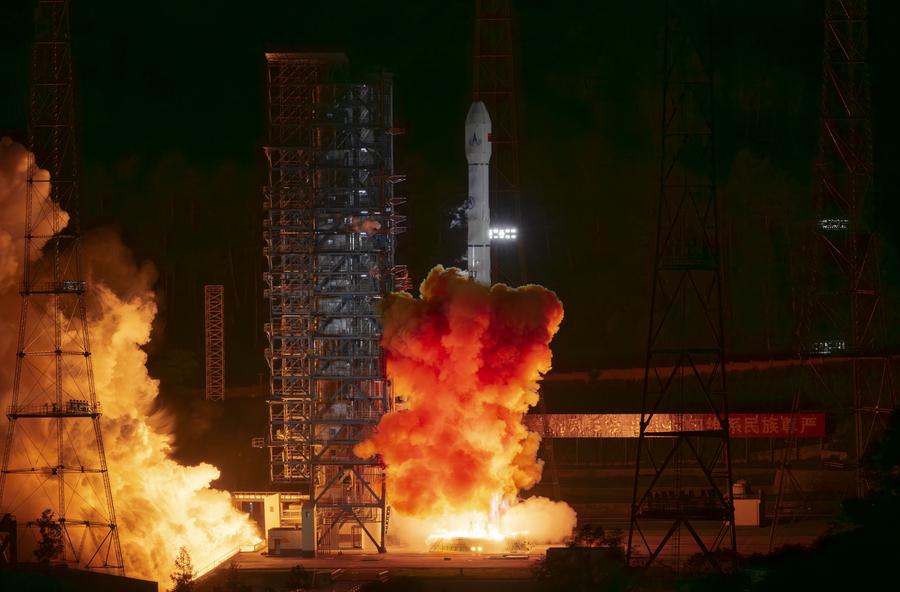


China launched its first asteroid sampling mission early on Thursday morning, aiming to explore a near-Earth small asteroid and retrieve its samples for scientists.
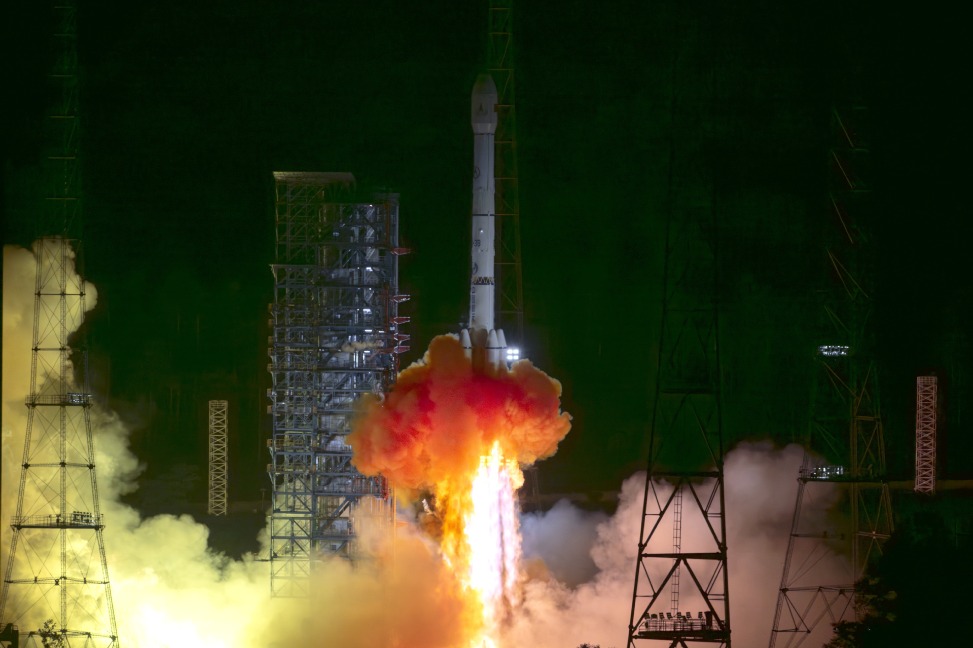
Carrying the Tianwen 2 robotic probe, a Long March 3B rocket blasted off at 1:31 am at the Xichang Satellite Launch Center in the middle of mountains in Sichuan province.
After flying for about 18 minutes, the rocket successfully deployed the Tianwen 2 into a transfer trajectory toward its destination, an asteroid called 2016 HO3.
The solar arrays of the probe then unfolded smoothly, marking the success of the launch phase, according to the China National Space Administration.
The CNSA stated that the Tianwen 2 mission is expected to achieve multiple objectives through a single expedition, including sample collection from 2016 HO3 and flyby exploration of main-belt comet 311P.
The administration said that mission planners aim to accomplish two major engineering goals through the Tianwen 2 project. The first is to develop and demonstrate key technologies needed for gathering sample from weak-gravity celestial bodies, conducting high-precision autonomous navigation and control, and other crucial maneuvers. The second is to obtain data and samples to facilitate studies on the origins and evolution of asteroids.
Scientifically, planners hope the spacecraft could measure multiple physical parameters of both 2016 HO3 and 311P, covering their size and shape, orbital traits, rotation patterns, and thermal radiation characteristics, allowing for research on their orbital dynamics. Researchers will also analyze their external features, material compositions, internal structures, and potential ejecta.
In the following year, the Tianwen 2 spacecraft, designed and built by the China Academy of Space Technology, is programmed to carry out several trajectory maneuvers to approach the 2016 HO3. After that, it is set to orbit the asteroid to perform remote observation and obtain data to enable scientists and ground controllers to analyze and determine suitable locations for the mission's most critical part: the sampling operation.
Following all preparations, the probe will approach the celestial body to gather samples.
If everything proceeds according to schedule, at the end of 2027, Tianwen 2 will fly back to Earth's orbit and release its reentry module, which will return to the ground with the samples.
After delivering the precious asteroid substances, the probe will utilize our planet's gravity as a slingshot to propel itself towards the comet 311P. It is expected to arrive at the comet several years later to conduct a detailed remote-sensing survey.
Once the samples are returned to Earth, they will be distributed to scientists for examination of their physical properties, chemical and mineralogical contents, and isotopic composition, contributing to studies on the formation and evolution of asteroids and the early solar system, according to CNSA.
2016 HO3, also known as 469219 Kamo'oalewa, was first spotted in April 2016 by an asteroid survey telescope at the Haleakala High Altitude Observatory in Hawaii.
The celestial body orbits the sun, remaining a constant companion of Earth. It is too distant to be considered a true satellite of Earth, but it stands as the best and most stable example to date of a quasi-satellite.
The analyses of 2016 HO3's reflectance spectrum and other physical characteristics have led to a hypothesis that this asteroid may be a boulder that was blasted off the surface of the moon following an impact with another space object.
China's initial excursion to an asteroid was a flyby of the ginger-shaped near-Earth asteroid named 4179 Toutatis in 2012, when the Chang'e 2 lunar orbiter made the pass as part of its extended mission.
Tianwen missions, named after an ancient Chinese poem, signify China's aspiration to explore other celestial bodies in the solar system beyond our moon.
The first in this series, Tianwen 1 was launched in July 2020, and it successfully touched down on Mars in May 2021. The probe deployed a rover named Zhurong to explore the Red Planet.
The next adventure, Tianwen 3, has been scheduled to be launched around 2028 to collect Martian samples and bring them back.