Scientists monitor surface solar radiation via satellite remote sensing

BEIJING -- A geostationary satellite network observation (GSNO) system has been developed to precisely monitor changes in surface solar radiation by introducing satellite remote sensing technology, according to the Aerospace Information Research Institute (AIR) under the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Serving like a "sunlight scanner," the GSNO system can provide more precise data support for sectors such as clean energy application, agricultural yield estimation and climate change response, as well as public health, said the institute.
The study was led by AIR researchers and conducted in collaboration with researchers from multiple institutions, both at home and abroad. The study results have been published in the journal The Innovation.
Surface solar radiation is a general term for the solar radiation components received by the Earth's surface, including ultraviolet rays, visible light, infrared and other electromagnetic radiation of different wavelengths. Therefore, it is a key factor affecting climate change, agricultural production and solar energy application.
"Satellite remote sensing technology features strong data continuity and wide coverage. It is one of the most effective means to monitor changes in surface solar radiation," said Husi Letu, AIR researcher and leader of the study.
Notably, the study team integrated multiple new-generation geostationary satellites into the GSNO system.
Through multi-satellite networking, this system has achieved high spatiotemporal resolution monitoring at a near-global scale with enhanced detection accuracy.
"At present, the GSNO system can provide near-global scale surface solar radiation monitoring data with a spatial resolution of 5 km and an observation frequency of once per hour," according to Shi Chong, an AIR researcher.
For example, short-wave radiation data can sustain the effective use of solar energy resources. Photosynthetically active radiation data can provide a new basis for agricultural yield estimation and ecological carbon sink estimation, while ultraviolet data is expected to be applied to public health, Shi explained.
- Scientists monitor surface solar radiation via satellite remote sensing
- China's top political advisor stresses democratic oversight over Yangtze River eco-environmental conservation
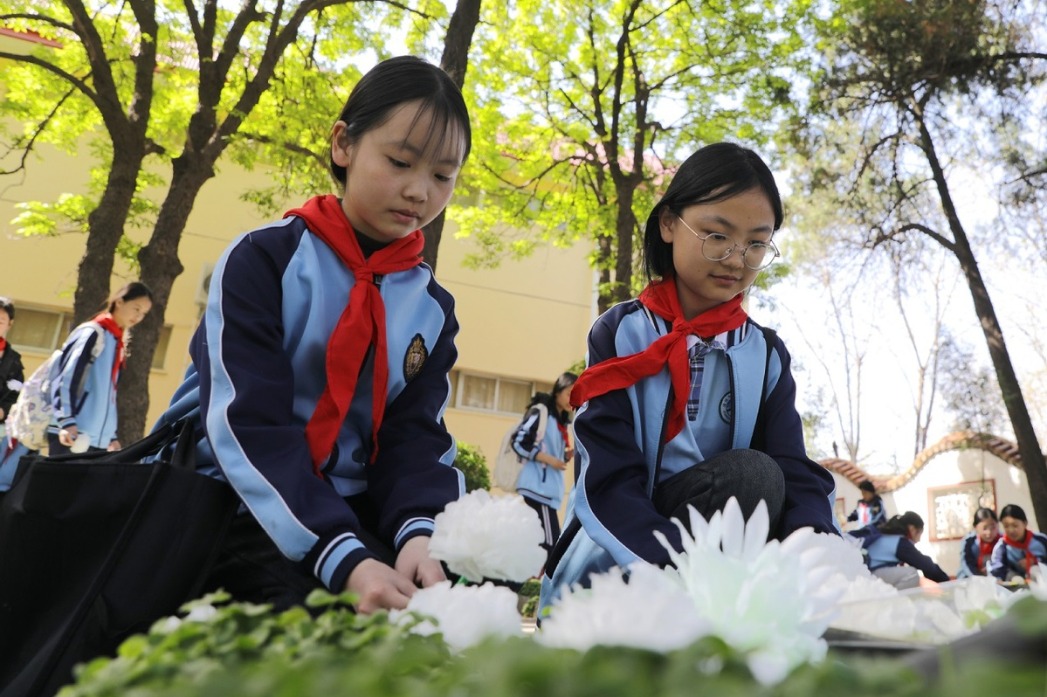
- People pay tribute to martyrs ahead of Qingming Festival
- Chinese vice-premier stresses boosting employment, entrepreneurship for college graduates
- Mainland's Taiwan affairs official meets with KMT vice-chairman
- Fudan team develops new kind of chips